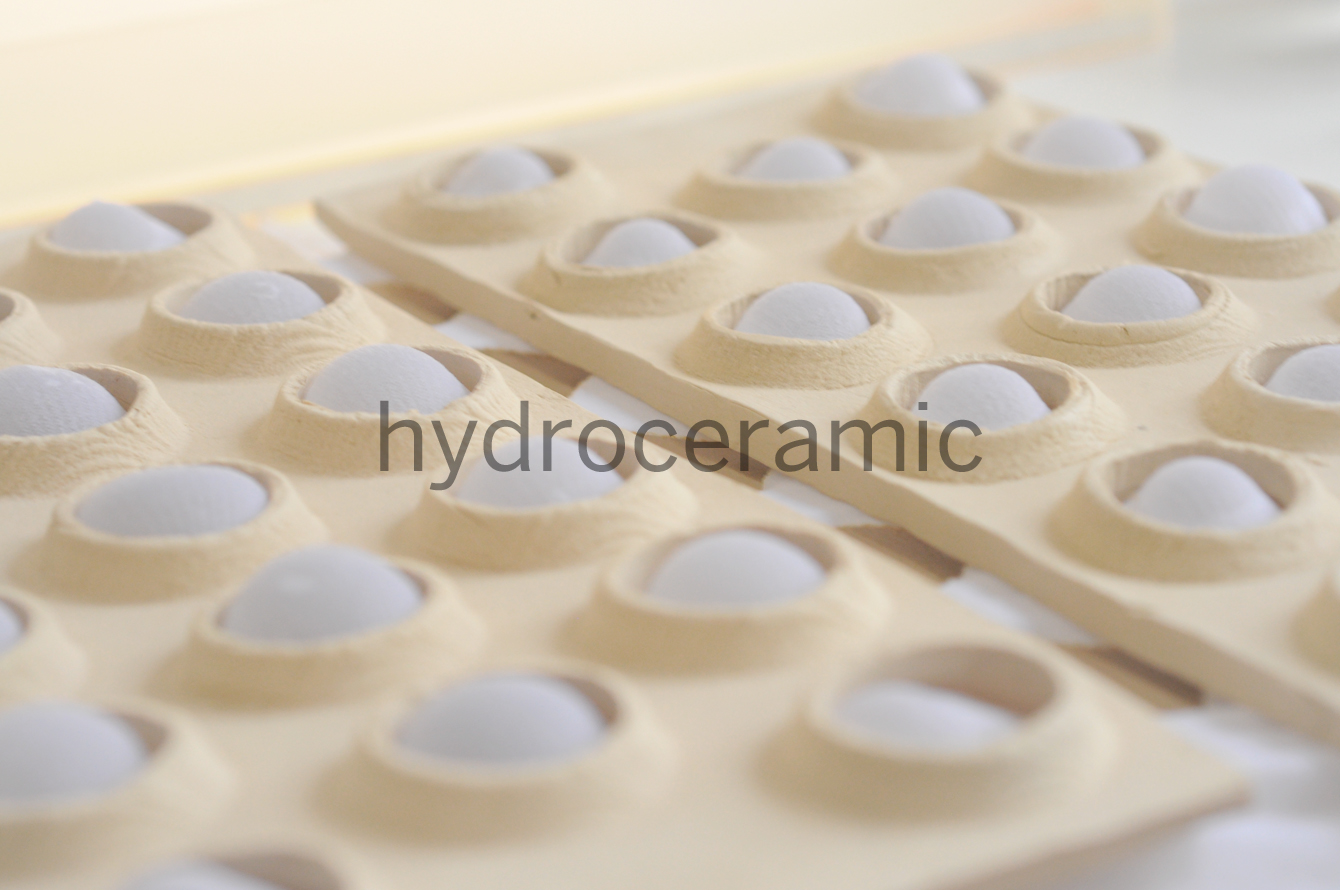
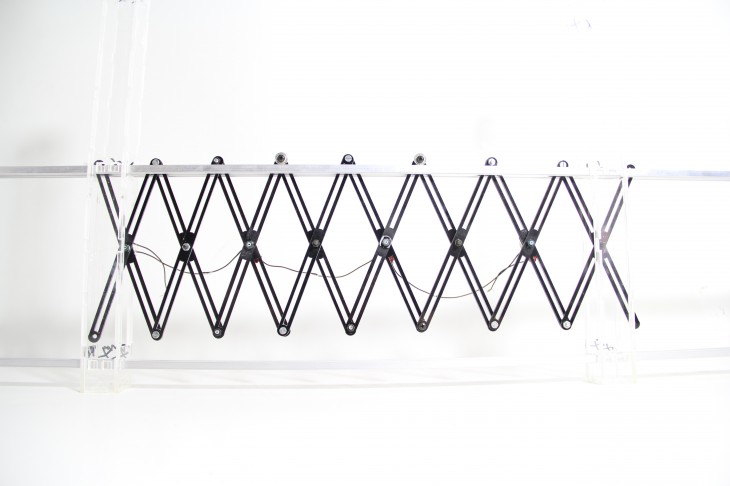
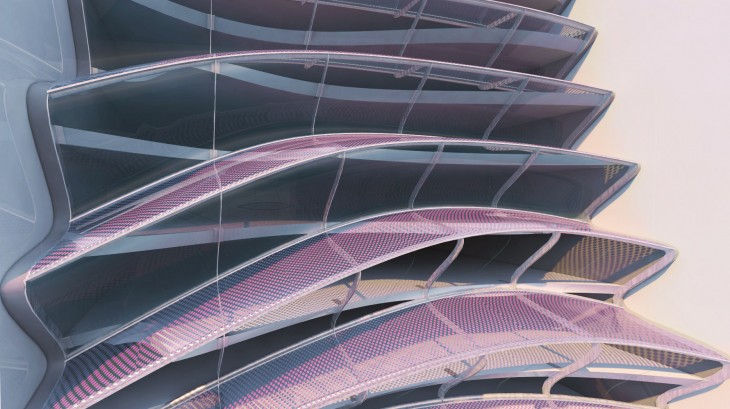
The research explores production methods and material behaviours in plastic biodegradable systems. It investigates DIY biomaterial production and passive reconfiguration processes to create components for a dissolving architecture. Our IBB catalogue presents a range of lightweight biobricks suited for low impact ephemeral structures undergoing passive distortion scenarios, until organic blending with the site is reached
The research explores production methods and material behaviours in plastic biodegradable systems. It investigates DIY biomaterial production and passive reconfiguration processes to create components for a dissolving architecture. Our IBB catalogue presents a range of lightweight biobricks suited for low impact ephemeral structures undergoing passive distortion scenarios, until organic blending with the site is reached
Bio-logical – In the first phase of the research we looked into material plasticity for programmable use. As part of a Life inspired and regenerative concept, we studied production feasability of biopolymers and their thermoplastic performance in passive+ and artificial systems. In the continuation of the project we further developped the idea of a malleable system, focusing on passive biodegradation with rainwater, or induced degradation by artificial moistening.
SimBIOsis – We define cycles of occupation from the material´s thermoplastic transformations. As a water sensitive composite system, its ability to partially dissolve and later absorb, allows deformability and reshaping of the structure. As the system becomes permeable, it can later on create opportunities for microhabitats to infiltrate the structure – Thus creating, an interface between large scale and microhabitats, and eventually forming a fully disintegrated foodbase for soil.
DEGRADABLE -
The biomaterial composite is devised for a metabolic approach. It is an ephemeral yet regenerating;
a repairable and easily perishable system that responds and feeds its ecosystem. Because of its thermoplastic properties, additional layers of material can easily blend with it – It can be refilled and reshaped. When used as a multilayered system with water resistant components, it can be restored following a controlled structure until the latter also biodegrades.
 The research explores production methods and material behaviours in plastic biodegradable systems. It investigates DIY biomaterial production and passive reconfiguration processes to create components for a dissolving architecture. Our IBB catalogue presents a range of lightweight biobricks suited for low impact ephemeral structures undergoing passive distortion scenarios, until organic blending with the site is reached
The research explores production methods and material behaviours in plastic biodegradable systems. It investigates DIY biomaterial production and passive reconfiguration processes to create components for a dissolving architecture. Our IBB catalogue presents a range of lightweight biobricks suited for low impact ephemeral structures undergoing passive distortion scenarios, until organic blending with the site is reached