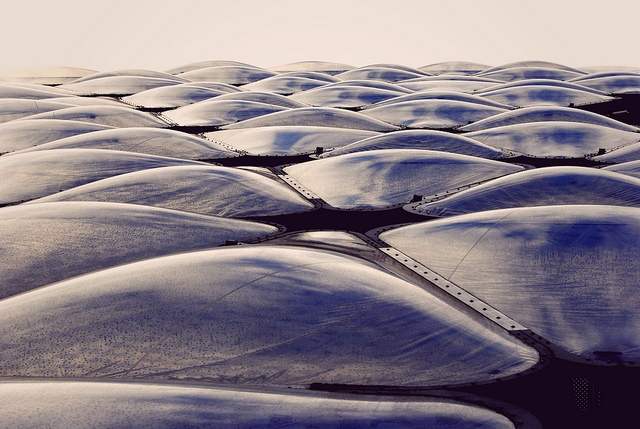
Case study: Watercube_Beijing National Aquatics Center_ PTW Architects, CSCEC, CCDI, Arup
Reading: On Growth and form_ D’Arcy Wentworth Thompson
Nature and the notion of organic have always been of much interest from architects designers and urban planners. Extensive theoretical studies, as well as architectural applications, have attempted to simulate nature, by extracting forms, geometries and principles found in living organisms.
The Beijing National Aquatics Center designed by PTW Architects, CSCEC, CCDI, and Arup is one of the most recent examples of applying natural systems in architectural design processes. In this building, vastly known as the Watercube, the strict geometry found in water bubbles was used as an inspiration for the exterior of the building, forming an iridescent cellular façade that diffuses natural light. The continuous skin, made by the ETFE material, was created as a steel structure housed in a cavity, filled by platonic solid units, that seem to be completely random, but in reality are different units that are repeated to the whole exterior of the building. The algorithmic relations that form the façade and roof of the Watercube, as well as the multiplicity of their units have been subject to great debate about the application of parametricism in architectural and urban design context.
The former principles of natural forms were long before theoretically analyzed from D’Arcy Wentworth Thompson in his book On Growth and form, almost a century ago. In his book, and particularly in the chapter On the Theory of Transformation, Or the Comparison of Related Forms, D’Arcy sets the basis of parametric design, at a conceptual level, through analyzing and comparing natural forms using mathematical justifications. The author explored the interrelations of growth, form and physical forces found in different relative species and the topological similarity of family variations, through grid and co-axial transformations and stretching of the natural geometries and structures of living organisms (leaves, fishes, animals, etc.). Though this study was carried out in a two dimensional level, it is implied that it can be extended into a three dimensional one, extrapolating important relations and principles between relative species, through breaking down the geometries at fractal basis. The notion of topology as a concept, that is evident in D’Arcy;s study, establishes a contemporary parametric design approach in a conceptual level.
As a future research, I would be highly interested in researching and comparing the new digital logics that are found in the recent parametric architectural examples, as well as exploring the relations that form them in a three dimensional level.
Image source: http://www.l-a-v-a.net/projects/beijing-watercube/